Overview¶
This section will provide guidance and usage on how to interact with Hubster’s APIs. The goal of Hubster is to provide a consistent and systematic approach across all our API resources, in terms of style, format and responses.
Hubster’s APIs are designed using REST principles and most of our payloads are structured using JSON. Any exception to this rule will be noted where necessary.
Note
Hubster APIs incorporate cross-origin resource sharing (CORS) whereby facilitating web applications to freely use our API in an authenticated and secure manner.
Environments¶
Below are the list of Hubster environments:
| Identity | API Resource |
|---|---|
| Demo | https://demo-identity.hubster.io |
| Production | https://identity.hubster.io |
| Portal | API Resource |
|---|---|
| Demo | https://demo-portal-api.hubster.io |
| Production | https://portal-api.hubster.io |
| Engine | API Resource |
|---|---|
| Demo | https://demo-engine.hubster.io |
| Production | https://engine.hubster.io |
| Events | API Resource |
|---|---|
| Demo | https://demo-events.hubster.io |
| Production | https://events.hubster.io |
Identity to API Resource Interaction¶
Below is a depiction on how a business application first obtains an access token, using Hubster’s identity service, which can later be used to make authenticated requests against API services, such as Hubster’s Portal, Engine and Events resources.
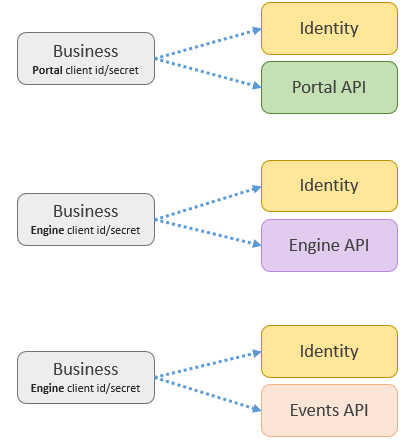
Note
API access tokens use the client_credential grant_type, Description you can only obtain a access tokens using client_ids and client_secrets respectively. These access tokens are longed-lived and last no longer than 30 days. When an access token expires, accessing an API resource yields an HTTP Status 401 - Unauthorized Access.
Furthermore, access tokens are only meant for their indented API resource. For example, if a business obtains an access token for the Portal API resource, the access token cannot be used for the to gain access to the Engine API resource, and likewise. These design was intentional as scopes for each API resource are vastly different. There’s an exception to this rule. Accessing the Events API requires an Engine access token.
To obtain an access_token, please refer to the Authentication API for more details.
Standard Error Response¶
Hubster’s standard error response model is consistent across all API resources. The only difference being are the actual error codes returned by each API resource.
Below is an example of a Bad Request (400) returned by the Portal API.
Response
{
"status": 400,
"errors": [
{
"code": 301,
"description": "Property 'name' is required. (code: PRT000301)"
},
{
"code": 206,
"description": "Value '50000' is not valid. (code: PRT000206)"
}
]
}
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| status | The HTTP Status code. This will value always equals header’s HTTP Status code. |
| errors | The list of errors. |
Paginated Results¶
In some cases, Hubster may return a paginated response whereby, the business will need to re-query the next result, based on page number and page size. This is typically when certain GET requests may yield a large number of records.
Below is an example from Portal API resource returning Hubs as paginated response.
Response : 200 (OK)
{
"pageNumber": 0,
"pageSize": 50,
"total": 2,
"results": [
{
"hubId": "00000000-0000-0000-0000-0000000000a2",
"tenantId": "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000001",
"name": "Dev Hub 1",
"description": "Dev Hub 1 (Websocket)",
"statusId": 2000
},
{
"hubId": "00000000-0000-0000-0000-0000000000a3",
"tenantId": "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000001",
"name": "Hubster Demo (blank)",
"description": "Hubster Demo mainly used for Videos",
"statusId": 2000
}
]
}
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| pageNumber | The requested page number. |
| pageSize | The requested page size. |
| total | The total number of results across all pages. Note: the total number of items does not necessary equal the number of result items. |
| results | A list of response models returned by the API resource. Note: the result models may differ on per call basis. |
HTTP Status Codes¶
Hubster API HTTP Status codes.
| HTTP Status | Description |
|---|---|
| 200 | OK response. The body of the response will include the data requested. |
| 201 | OK response. The response will content no data. |
| 400 | Bad request. The body of the response will have more info. |
| 401 | Unauthorized. Token is invalid. |
| 403 | Forbidden. Access to the requested resource is forbidden. |
| 404 | Not found. Resource not found. |
| 408 | Timed out. The request timed out. |
| 409 | Conflict. The request caused a conflict. |
| 410 | Not available. The request is not available. |
| 417 | Expectation Failed. The operation was aborted. |
| 429 | Too many requests. API usage limit has been reached. |
| 500 | Internal server error. There was an internal issue with the service. |
| 501 | Not implemented. The request is not implemented. |
| 503 | Service unavailable. The service is unavailable. |